If you run a business—whether it’s a tiny startup or a growing enterprise—you already know how much depends on the numbers. But what you may not know is that all those numbers fall into just three main buckets.
These three key areas of accounting help businesses track performance, follow the rules, and plan ahead. Get these right, and you’ll make smarter decisions, avoid costly mistakes, and stay in control of your money.
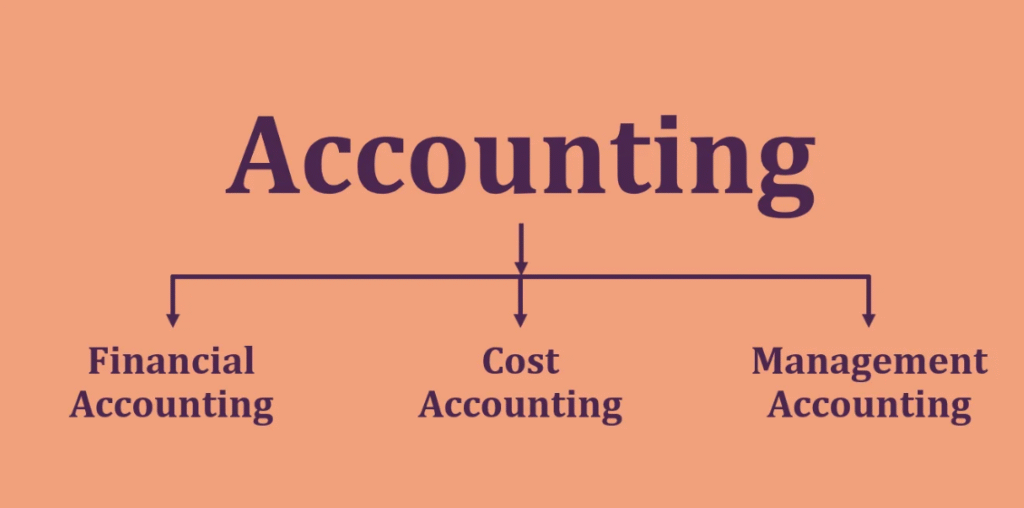
Let’s break them down in a simple and practical way.
1. Financial Accounting: The Language of External Reporting
Financial accounting is what you show the outside world.
This area deals with recording, summarizing, and presenting financial transactions in a structured format. Think income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
These reports are used by investors, regulators, lenders, and others to understand how your business is doing. So, accuracy and transparency are non-negotiable.
Financial accounting follows standardized rules—usually Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) depending on the region. These standards help ensure the data is consistent and comparable across businesses.
Key features:
- Tracks revenue, expenses, assets, and liabilities
- Follows strict guidelines and formats
- Used for audits, tax filings, and investor reports
- Usually done quarterly or annually
Example:
If you’re applying for a business loan, the bank will want your financial statements. That’s financial accounting at work.
2. Managerial Accounting: The Tool for Internal Decisions
Unlike financial accounting, managerial accounting is just for your internal team.
It’s all about using financial data to help managers make smart choices—every day. There’s no formal format or external standard here. The goal is clarity and usefulness, not formality.
This area covers budgeting, forecasting, cost analysis, and performance reviews. Whether you’re deciding how much to spend on marketing or how to price your products, managerial accounting gives you the answers.
Key features:
- Helps with business planning and strategy
- Focuses on cost behavior, break-even points, and profit margins
- Can be as detailed and flexible as needed
- Often updated monthly, weekly, or even daily
Example:
Wondering if you should hire two new employees or outsource a project? Managerial accounting helps you crunch the numbers.
3. Tax Accounting: Staying Compliant and Efficient
Taxes aren’t optional. But overpaying them? That can often be avoided—with the right tax accounting.
Tax accounting focuses on everything related to your business’s tax obligations. This includes calculating taxable income, taking deductions legally, filing returns properly, and meeting deadlines.
Different countries (and sometimes regions) have different tax laws, so businesses need to stay updated on what applies where they operate. Good tax accounting helps you comply with local laws and save money where you can.
Key features:
- Follows local tax codes, not financial reporting standards
- Deals with income tax, VAT/GST, payroll tax, and others
- Helps avoid fines, audits, and interest charges
- Focuses on minimizing liability legally
Example:
If your business made a profit last year, tax accounting figures out how much you owe—while making sure you claim every eligible deduction.
Quick Comparison Table
| Area | Main Focus | Who Uses It | Follows Rules? |
| Financial Accounting | Reporting to outsiders | Investors, lenders, tax agencies | Yes – GAAP/IFRS |
| Managerial Accounting | Internal decision-making | Business owners, managers | No – internal use only |
| Tax Accounting | Filing and saving taxes | Government, tax preparers | Yes – local tax laws |
Why These 3 Areas Matter
Each area of accounting serves a different purpose.
- Financial accounting keeps you accountable.
- Managerial accounting helps you grow.
- Tax accounting keeps you out of trouble.
You can’t really run a business successfully without covering all three.
Whether you do it all in-house or hire professionals, make sure these areas are handled well. It’s not just about avoiding mistakes—it’s about creating a business that runs smoothly and grows with confidence.
Conclusion
Accounting might seem complex, but when you break it down, it’s really about understanding your business better.
These three major areas—financial, managerial, and tax accounting—are the backbone of smart business management. They help you stay honest, make informed decisions, and meet your legal obligations.
Whether you’re just starting out or scaling up, knowing how these three work (and using them well) can be the difference between surviving and thriving.
So take them seriously. Your business deserves that kind of clarity and control.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the same accountant for all three types of accounting?
A: Yes, many professionals handle all three. Just make sure they’re qualified and understand the specific requirements of each area.
Q: What happens if I ignore one of these areas?
A: You risk making poor decisions, facing tax penalties, or losing trust with stakeholders. All three areas work together to keep your business healthy.
Q: Do all businesses need to follow GAAP or IFRS?
A: No, only businesses that report to external entities or are publicly accountable usually need to follow these standards. For smaller or private companies, it depends on local regulations.
Q: How often should I update my financial records?
A: Ideally, you should keep them up to date regularly—monthly is common. Waiting until year-end often leads to errors and missed opportunities.
Q: Is accounting software enough, or do I still need a professional?
A: Software helps, but it doesn’t replace expert insight. A professional can catch things software might miss and help with complex tasks like tax planning and strategic budgeting.